Carboxytherapy
Carboxytherapy refers to the cutaneous and subcutaneous administration of carbon dioxide gas [CO2] for therapeutic purposes. Carboxytherapy originated at the Royal Spas of France in 1932 with the treatment of patients afflicted by peripheral arterial occlusive disease. In South America and Europe, carbon dioxide therapy has been applied to the treatment of stretch marks, cellulite, and hypertrophic scars with impressive results. Studies have demonstrated that carboxytherapy improves skin elasticity, improves circulation, encourages collagen repair, improves the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and destroys localized fatty deposits. There are no known risks associated with carboxytherapy. Carbon dioxide injection.
Carboxytherapy – The Mechanics
Carbon dioxide is present in our bodies at all times. We breathe in oxygen, and we exhale carbon dioxide. Plants take up the carbon dioxide, and in turn give us the oxygen that we need. Carbon Dioxide also happens to be the signal for poor blood circulation in the body. All cells in the body, regardless of their job (heart cells, brain cells, skin cells) release as their waste product carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is the “cost of doing business” of any cell in our bodies. So, we breathe in oxygen to our lungs, the red blood cells pick up the oxygen in our lungs and carry it to our tissues until they encounter an area that has been working hard and has an excess of carbon dioxide. When the blood cells are exposed to high concentrations of carbon dioxide, they flip their conformation, release the oxygen molecules, and pick up the carbon dioxide so that we can exhale it from our lungs. In a sense, by injecting small amounts of carbon dioxide gas just below the surface of the skin, we are tricking it into increasing the blood circulation to that area. Dark under-eye circles, cellulite, and stretch marks have all been shown to have some root cause in poor blood circulation.
Carboxytherapy for Stretch Marks
Stretchmarks are characterized by wide linear bands of discolored or wrinkled skin that occurs in areas of collagen damage due to stretching. Striae are usually found on the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, and breasts. Women develop striae more commonly than men, and striae are seen in 90% of pregnant women due to a combination of hormonal factors along with increased stress on the collagen and elastin in the skin. Some studies indicated that striae are a form of scar tissue that forms in response to collagen rupture and elastic fiber changes. Two types of striae are described, newly formed, reddish colored and older, white striae. The treatment of old striae has been challenging and various modalities have been studied. These include topical retinoids (Retin A), microdermabrasion, intense pulsed light (IPL) and fractionated laser skin resurfacing. Although striae are thought to be a result of collagen rupture and breakdown during stretching of the skin, until recently, few treatments actually targeted the root cause of the striae formation, the damaged collagen in the dermal layer. Furthermore, laser and light modalities are not safe for individuals with darker skin tones. Carboxytherapy is the only treatment available for both old and new stretchmarks that visibly repairs the broken collagen and is safe for all skintypes. Carboxytherapy causes the formation of new collagen and subsequently thickens the skin to improve the appearance of the stretchmarks by rebuilding the collagen matrix.
Carboxytherapy for Cellulite
Cellulite refers to the lumpy fat bulges on the thighs and buttocks of over 95% of the normal female population. There are many reasons why most women are predisposed to cellulite whereas the condition is much rarer in men. To begin with, the underlying structure of the skin is different in males verses females. Male skin tends to be thicker and the fibrous septae has strong cross-linking of the connective tissue. Females have thinner skin and no cross-linking of the underlying septae. Women have more fat layers than men, and the subcutaneous fat layer in women is regulated by hormones and does not respond to diet and exercise. The female hormone estrogen causes these fat cells to store fat, whereas the male hormone testosterone stimulates the fat cells to break down fat. So, women are genetically superior at storing energy in the form of fat to provide energy during pregnancy. Women also have a higher percentage of body fat in the areas of the thighs, hips, and abdomen, and these fat cells are resistant to diet and exercise. Directly beneath the fat layer there is a layer of connective tissue comprised of collagen called the “fibrous septae.” When the fibrous septae becomes damaged, the subcutaneous fat cells are pushed through the damaged regions and are squeezed into small bulges that give the overlying skin the “puckered” or “dimpled” appearance that we call cellulite.
Women have tried numerous therapies to eliminate their cellulite including various creams, massage, etc to no avail because none of these therapies correct the underlying physiological problems of poor circulation and damaged collagen septae. Two therapies that have shown promise in eliminating this difficult problem are the Thermage CL cellulite tip and carboxytherapy. Carboxytherapy was originally used for aesthetic purposes by the Brazilians to sculpt residual post-liposuction fatty deposits above the knees and histological studies showed that the fat cells were ruptured by the CO2 gas while leaving the remaining skin structures and nerves unharmed. Collagen remodeling was also shown to occur, as well as thickening and smoothing of the overlying skin.
Carboxytherapy for Dark Undereye Circles
Carboxytherapy can dramatically improve the appearance of dark under-eye circles. Although sometimes caused by darkened pigment, or a hollow depression below the lower eyelids [tear trough deformity], the majority of dark under-eye circles are caused by poor circulation beneath the lower eyelids. At Plastic Surgicentre we use carboxytherapy for rejuvenating the under- eye region. by injecting a small amount of carbon dioxide gas just beneath the skin of the lower eyelid, circulation will increase and dark under-eye circles will markedly improve. The treatment takes only five minutes, and is virtually painless and risk-free. A series of 2-6 treatments spaced one week apart is all that is required to achieve a great result.
Ultraformer
ULTRAFORMER NON SURGICAL FACE LIFT
WHAT IS ULTRAFORMER ?
A non-surgical face and neck lifting treatment, which uses a multi functional High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) technology. This technology is effective in lifting and tightening the skin on the face & body. The Ultrafromer II treats the face and neck, the Ultrafomer III treats the face, neck and body.
The treatment is non-invasive, with no downtime but the results have a surgical like result. This is a short treatment taking less than an hour.
What does the Ultraformer treat?
Neck wrinkles/Turkey Neck
Frown lines
Crows feet
Jawlines
Nasilabial folds
Eyebrow lift / Sagging eyelids
Double chin
Fine lines & Wrinkles
Uneven skin tone & texture
Enlarged pores
Post pregnancy tummy tightening
Skin tightening
1.5mm, 3.0mm and 4.5mm interchangeable cartridges are used for facial treatments, deeper depth cartridges are used for the rest of the body.
DURING TREATMENT
There is a little discomfort associated with this treatment, it varies from patient to patients. Most patients withstand the procedure without any anesthesia.
POST TREATMENT?
Post treatment there will be a little redness and slight bruising, this could last anything from minutes to a couple of days, dependant on the areas treated and the depths used.
IS IT BETTER THAN SURGERY?
The ULTRAFORMER is a great alternative to surgery, it carries far less risk, non-invasive with no downtime. ULTRAFORMER effectively treats the superficial and deeper dermis in addition to SMAS with the triple layer lifting effect.
HOW LONG DO THE RESULTS LAST?
Patients can see some immediate effects, improving over 2-3 months and can last from 6-12 months.
WHAT KIND OF TECHNOLOGY DOES THE ULTRAFORMER USE?
The ULTRAFORMER uses MF HIFU (Multi Functional High Intensity Focused Ultrasound). MF HIFU affects various layers of the superficial dermis, deep dermis, fat layers including the SMAS (Superficial Muscular Aponeurotic System). The SMAS are the deeper layers which in a surgical face lift a surgeon would lift under the knife. MF HIFU is a thermal energy which safely heats the tissue, this causes the skin to tighten and form new collagen providing long term skin tightening.
Plastic Surgery For Men
Men and cosmetic surgery
Our society places a high value on looking young and fit. Today, men of all ages and all walks of life are requesting plastic surgery for cosmetic reasons. Men’s goals include a more balanced nose, a rejuvenated face, a trimmer waistline. The procedures used to achieve these goals must take into consideration factors such as skin thickness, beard growth, or body type.
Facial surgery
In general, it’s known that male facial skin has a richer blood supply than female facial skin. Male faces bleed more during surgery and are at greater risk for forming a temporary collection or pooling of blood under the skin, called a hematoma, after surgery. Also, any scarring that may result from surgery may be more difficult for men to hide, since they don’t wear make-up or style their hair toward their faces, as many women do. Hair growth and beard growth may play a major role in the outcome of a facelift. If you are balding or have thinning hair, surgical artistry may be required to hide the facelift incision, especially in the temple area. If the hair-bearing skin of your upper neck is pulled behind your ears during surgery, you may find that you must shave behind your ears or the back of your neck. However, sometimes electrolysis can correct this problem. A fatty or “jowly” area beneath the chin is also a concern for many men. In younger patients, liposuction alone may be sufficient to correct the problem. Older patients may require a full facelift and necklift, which may include the removal of excess skin and tightening the platysma muscles, which run down each side of the neck. These muscles are usually thicker in men than they are in women, but do not pose a greater challenge for your plastic surgeon.
“Refinishing” treatments for facial skin: Shaving must be postponed for about 3 weeks after a skin-smoothing treatment such as chemical peel or dermabrasion. Because these procedures strip away the surface layers of skin, you can expect your face to remain sensitive, swollen, and bright pink for several weeks following surgery.
Gynecomastia
Breast reduction surgery for men. Enlarged male breast is quite common and affects one or both sides of the chest. Removal of fatty tissue and skin will reduce and firm up surrounding tissue.
Gynecomastia is a condition in which males develop enlargement of the breast. Male breast enlargement is often seen during puberty but commonly resolves spontaneously. In those cases where the male breast remains enlarged surgery may be indicated.
Gynecomastia is quite common in adolescents and is often first noted at the onset of puberty. The medical literature reports rates as low as 8% and as high as 65%.
Most of these cases are due to changes in the hormonal secretion with temporary excess of estrogen like substances or relative deficiencies of testosterone like substances. This imbalance can lead to temporary increases in the amount of ductal tissue present on one or both sides. The majority of cases show enlargement in both sides. The degree of enlargement varies widely but in the most severe cases C or D cup breasts may be present. The milder cases usually resolve in 3 months to a year although it is not unusual to see some breast enlargement for up to three years. By the late teens most of these patients will have normal appearing male breasts without any form of treatment. Because young boys are reluctant to discuss their concerns they are likely to simply try to hide their abnormal appearance with clothing. They may try to avoid gym classes, athletic activities, and swimming or beach activities.
While most gynecomastia is seen in adolescence and resolves without treatment some cases are the result of endocrine gland malfunction or tumors. Some types of liver disease and cancers of several types can produce gynecomastia.
Some cases are due to congenital syndromes and others may be related to drug use such as steroids or marijuana. There is a second peak in incidence late in life and here the risk of ductal carcinoma of the breast must be a stronger consideration so that biopsy of the breast may be necessary.
When gynecomastia is severe, when it persists, and in those cases where there is suspicion of malignancy surgical treatment may be indicated.
In most cases the incisions for this operation can be placed just inside the areolar border where they are less likely to be conspicuous. The glandular tissue must be removed. This firm fibrous tissue extends from the nipple areolar complex down to the surface of the pectoral muscle beneath. In some cases it is helpful to use liposuction to remove some of the fatty tissue which always surrounds this ductal tissue. Without this liposuction some patients would have a “donut” shaped defect after removal of the ductal tissue.
Complications
The most common complication following surgical removal of the ductal tissue is hematoma. When severe this could lead to a second operation to drain the collection of blood . Some residual deformity of the nipple areolar area may remain despite the best efforts of the surgeon. With any operation a wound infection could occur. Inadvertent injury to the blood supply of the nipple areolar region could result in loss of skin in the nipple areolar area.
There would be the usual anesthetic risks associated with any surgical procedure. These complications and other even rarer complications do not occur often and the vast majority of patients undergoing this operation are very pleased and adopt a more normal life style with regard to exposure of the chest in normal social situations such as the beach.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Thermage
Aging affects us all – the way we act, the way we feel, and definitely the way we look. But with advancements in skin care, you can have a say in the way aging affects your skin – and maybe even get back to the way you looked not so long ago. Thermage is a proven, unique radiofrequency treatment that can help improve the appearance of sagging or loose skin, giving you a smoother, sleeker and younger look and feel. Thermage works in just one treatment with little down time and delivers a natural looking result. It’s you, just younger looking and more confident
Thermage is effective on:
The Eyes – hooding, fine lines and even our brow line can make us look worn-down. Thermage treats the upper and lower eyelids to help you look more youthful and rested
The Face – as we age, phrases like “turkey neck”, loose jowls, sagging skin and “what happened to my jawline?” creep in. Thermage smooths lines and wrinkles and remodels collagen for the overall health of the skin
The Body – aging doesn’t just affect the skin on our faces, our bodies see the effects too, with creepy, sagging skin and unwanted bulges and dimples. Thermage is a non-invasive way to smooth the skin on our bodies and even temporarily improve the appearance of cellulite.
HOW THERMAGE TREATMENTS FIT
Thermage is for when you want to tackle the effects of aging on your skin. You want to look younger and you want real results – but don’t want the overly drastic change or extended downtime that comes with surgery. Thermage fits into any lifestyle and your current beauty regimen:
* A single treatment that delivers results
* Non-invasive and clinically proven to be safe
* Minimal downtime, so it’s easy to fit into your routine
* Real change you just can’t get from lotions and creams
* Targeted, effective treatment that can help address the signs of
* aging on many areas of the body
Laser Hair Removal
 Laser hair removal is commonly performed at plastic surgicentre in Doha, Qatar.
Laser hair removal is commonly performed at plastic surgicentre in Doha, Qatar.
Hair Today, Gone Tomorrow!
Say goodbye to painful waxing, shaving and plucking. Unwanted body and facial hair no longer has to be a concern. At Dr Makki clinic we provide the latest in hair removal services.
Which Treatment Is Best For You?
Patients with dark hair and light skin respond best to lasers. Call for a consultation to decide which treatment option is best for you. Even the most extensive areas such as facial hair, underarms, bikini line, shoulders and backs can now be treated. In just a few treatment sessions using the gentle power of lasers, you can have smooth, hair free skin you always dreamed of.
Start Today to Discover the Beauty of a Figure That Inspires Self-Confidence.
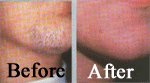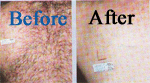
Hair Removal
Eliminating Unwanted Hair Safely, Permanently, And Comfortably
In our culture, excess body hair in women can be embarrassing. Although shaving is acceptable to men, women who shave their faces just do not fit the image of a woman. The latest technology for removing hair is less painful and more effective and has eliminated scarring.
Start Today to Discover the Beauty of a Figure That Inspires Self-Confidence.
For years women have tried many methods for removing hair from their body. Bleaching, waxing, and tweezing are temporary solutions for battling excess hair. laser is the only permanent solution for hair removal. New technologies have produced more satisfied patients. Men have also found these newer techniques effective for unwanted hair on their ears, neck, shoulders, and back. A private consultation will answer your questions.
Gentlelase Laser Hair Removal
“Gentlelase With Integrated Dynamic Cooling Device Gaining Wide Acceptance”
What Is The Candela Gentlelase And Why Is It A Safe Treatment?
Lasers have been used for several years for a variety of medical cosmetic procedures including treatment of facial and leg veins, age spots, tattoos, and birthmarks and smoothing fine lines on the face. The Gentlelase, a revolutionary long pulse high energy alexandrite laser system, emits a gentle beam of light that passes through the skin, to the hair follicle where it is absorbed. The laser energy is transformed into heat, which can disable the follicle, leaving the surrounding skin unchanged. The skin is further protected during treatment by a dynamic cooling process where a cryogen is sprayed onto the skin cooling the upper layers providing patients increased comfort. This selectivity helps to protect the skin while effectively treating the unwanted hair.
What Conditions Are Treated With The Laser?
Traditional hair removal techniques, such as shaving, plucking, and waxing, provide only temporary relief. Until now, the only semipermanent way to remove hair has been by electrolysis. The Gentlelase safely removes unwanted body hair without damaging the delicate pores and structures of the skin. Facial and bikini areas are usually completed in under 10 minutes; legs and larger areas can take longer.
Why Should I Have Gentlelase Treatment?
This is a procedure to remove unwanted hair. The best results have been achieved on darker, finer hair, but other factors may influence the treatment process and are generally best evaluated and discussed during a consultation. The Gentlelase offers safe and effective treatment.
How Many Treatments Will I Need?
Hair grows in cycles. The number of treatments required depends on your skin, hair coloring, and coarseness of the hair. Everyone will require at least three to four treatments as the process is only effective on hairs during their growing cycle. Repeated sessions will be necessary to treat these follicles when they re-enter the growth phase.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is commonly performed at plastic surgicentre in Doha, Qatar.
Mesotherapy is the practice of using microinjections of conventional or homeopathic medication and/or vitamins into the mesoderm or middle layer of skin to deliver healing or corrective treatment to a specific area of the body. Mesotherapy has been touted as the latest breakthrough for body sculpting, cellulite reduction and skin rejuvenation. Why? Because it works!
Mesotherapy for Cellulite (Meso)
The Medical Term for Cellulite is Dermatomyoliposclerosis (DMLS)
Cellulite is a skin condition affecting over 90% of most post-pubescent women. Even those with a slim figure often complain about cellulite’s external visible symptoms — its lumpy, dimpled appearance. Cellulite commonly appears on the hips, buttocks and legs, but is not caused by being overweight, as many believe.
Cellulite appears in the subcutaneous level of skin tissue. Fat cells are arranged in chambers surrounded by connective tissue called septae. As water is retained, fat cells held within the perimeters of this area expand and stretch the connective tissue. Eventually this connective tissue contracts and hardens (sclerosis) holding the skin at a non-flexible length, while the surrounding tissue continues to expand with weight, or water gain. This results in areas of the skin being held down while other sections bulge outward, resulting in the lumpy, ‘cottage-cheese’ appearance.
Effective treatment of cellulite is considered the “homerun” of the cosmetic world. Nothing, and I mean nothing, even comes close to the results that mesotherapy gets with cellulite. Plastic Surgicentre is pleased to specialize in the only known effective treatment to date for cellulite. For more information on mesotherapy or to schedule a consultation, please contact us.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Laser tattoo removal
Tattoo removal presents a difficult scenario to the treating physician. Tattoos may be accidental, caused by dirt or foreign material being driven into a wound, or they may be purposely applied in either an amateur or professional setting by using a varied number of inks and techniques. Successful removal of the latter type of tattoo is dependent upon its cause, size, method of placement, and type of pigment. Very small tattoos that seldom “show” are often best treated by simple excision and closure. A scar will result, but the scar is often less objectionable than the tattoo itself. Historically, physicians have treated larger, multicolored, purposely applied tattoos in two ways:
Dermabrasion–sanding the skin down below the level of the tattoo ink
Carbon dioxide laser vaporization of the entire tattooed area
In most patients, these treatments result in objectionable scars. Today, we remove tattoos with a type of laser known as a Q-switched YAG laser. This laser fires a very intense beam of light, either invisible or green colored, into the tattoo in a very rapid burst. This heats the pigment within the tattoo and triggers its eruption from the skin. The laser color is chosen dependent upon the color of the ink–certain colors, like fluorescent yellow, are extremely difficult to remove. The procedure time varies from 15 to 45 minutes, depending on the tattoo size and the area treated. Topical anesthesia is occasionally used depending on tattoo location, size and the patient’s tolerance for the brief burning discomfort associated with each laser burst. Oral or intramuscular sedation can be used at the patient’s request. Following treatment, the wound may ooze small amounts of blood for several hours. The wound must be covered with a dressing for 24 hours and maintained in a moist environment for seven to 10 days. The risks of scarring with this treatment are quite low. However, complete eradication of the tattoo is quite rare. Although multiple treatments are usually required to obtain successive lightening of the tattoo, final results are dependent upon the depth of the tattoo pigment within the skin. On rare occasions, certain uncommon tattoo inks react with the laser to form a darker-colored chemical which is untreatable. While some small amounts of pigment may remain, the average patient is quite happy with the improvement obtained. Although multiple treatments are required, the risk of the procedure is quite low.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Endermologie (Cellulite treatment)

State of the art equipment
Endermologie® is an amazing cellulite-reduction program that uses advanced technology—a combination of state-of-the-art mechanical massage and suction— to help produce a slimmer, trimmer body while eliminating the cottage-cheese appearance of cellulite. Endermologie® makes it possible to reduce the appearance of cellulite, produce a marked improvement in skin tone, and a decrease in the circumference of body areas after only a few weeks. Endermologie® is a nonsurgical, noninvasive procedure using rollers and suction to produce a deep, stimulating massage that increases blood flow to the body zones where help is needed.
Start Today to Discover the Beauty of a Figure That Inspires Self-Confidence.
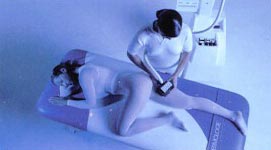 Smooth Bumpy Uneven Skin
Smooth Bumpy Uneven Skin
Reshape Buttocks, Thighs and Abdomen
Relieve Minor Muscle Aches and Pains
Increase Circulation
Reduce Circumference of Your Problem Body Areas
Reshape Your Body After Pregnancy
Relax Away Muscle Spasms
It reshapes body areas.
It smoothes the “cottage-cheese” appearance of the skin.
It is safe.
It is painless.
It is non-surgical and non-invasive.
It works where diets and exercise fail.
It is FDA-approved.
It effectively reduces the appearance of cellulite.
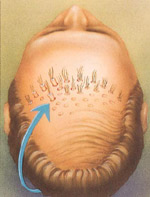
Hair Transplant

Hair replacement candidates should have some noticeable hair loss with healthy hair growth at the back and sides of the head to serve as donor areas.
Hair loss is primarily caused by a combination of aging, a change in hormones, and a family history of baldness. As a rule, the earlier hair loss begins, the more severe the baldness will become. Hair loss can also be caused by burns or trauma, in which case hair replacement surgery is considered a reconstructive treatment, and may be covered by health insurance.
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure in which small plugs (varying from Micrografts to Full Grafts) of hair bearing skin containing 2 to 15 hairs each are taken from the sides or back of the scalp and implanted to the bald area on the head, or bald areas are removed and hair growing spots are sewn together.
Surgery generally takes a few hours. It can often be done under local anesthesia, similar to going to a dentist.
May require multiple treatments over 18 months or more. Works best on men with male pattern baldness after hair loss has ceased.
Hair Transplantation is remarkably safe. There are occasional problems with delayed healing, infection, scar spreading, graft loss, etc. but major complications are quite rare. Excessive activity in the first few days can cause some of the plugs to be “ejected” from the scalp but this is quite uncommon with proper care, and poses no risk to your health.
Recovery after each procedure is usually rapid. Following the procedure, you are required to wear a protective bandage overnight. There is moderate discomfort in the scalp for the first day or two, and you may experience a headache which is controlled with oral medication. Some swelling and bruising around the eyes may occur two to three days after surgery, especially following extensive grafting. Using eye compresses and sleeping in a semi-reclining position can minimize these problems. The grafts “stick” pretty quickly, but it is possible to dislodge them with vigorous excercise, scalp massage, etc. until they are healed in. Smaller grafts (mini and micro) are less likely to pop out. Scabs may be present on the grafts for seven to ten days. Numbness around the donor and the recipient sites is common and will diminish within two to three months.. Small scars remain but are hidden within the hair line.
About six weeks after the transplant, the transplanted hair begins to fall out. Approximately three months later, new hair appears and grows at about the same rate as it did in its original location, about one-quarter to one-half inch a month. One to three months later, the spaces between the new implants are filled in with new grafts. Several treatment sessions may be necessary and patients who want to achieve greater density or refinement of the hairline often return for additional transplants. Refinement of the hairline is accomplished through the use of micrografts, minigrafts or single hair grafts. In this procedure, grafts containing only a few fine hairs are used to fill in small spaces. More extensive use of these micrografts blend in with the coarser hair to produce a hairline similar to the patient’s original one, therefore, giving a more desired natural appearance.
Hair replacement surgery can give a look of a full head of hair, but it cannot perform miracles. With balding, there is a loss of the full, thick strands of hair that we usually see on the head, and they are replaced by fine, silky, white hairs. The hair follicles remain, but they no longer produce the larger, thicker, darker hairs that we desire. A typical head of hair has about 100,000 hair follicles. With baldness, there is a loss of hairs, but this loss occurs in specific areas (the top of the head). As the baldness progresses, there is progressive loss of hairs, but the areas on the side continue to grow.
Hair transplantation involves moving the hair follicles from the sides, where they will always grow, up to the areas where the hair is thin. These transplanted follicles grow hair just as they would have in the area that they were taken from, and do not “fall out” like the other hair that started there. This phenomenon is called donor site dominance, and this explains why hair transplantation works.
It is certainly possible to give the illusion of a full thick head of hair in most cases. On the other hand, there is a decrease in the total number of hairs on the head, and so there has to be some compromise made. The hair can be “diluted” to cover the whole head, or it can be made more concentrated in some areas and more thin in others (this is what is generally done). The forehead hair line is generally made thick, and the hair behind it over the crown is left a bit thin. This gives the illusion of full hair, even though the total number of hairs is diminished.
Hair Replacement Surgery
Hair replacement candidates should have some noticeable hair loss with healthy hair growth at the back and sides of the head to serve as donor areas.
If you’re considering hair replacement surgery, the following information will give you a basic understanding of the variety of procedures involved. It can’t answer all of your questions, since a lot depends on your individual circumstances. Ask your surgeon if there is anything you don’t understand about the procedure you plan to have.
The truth about hair loss
Baldness is often blamed on poor circulation to the scalp, vitamin deficiencies, dandruff, and even excessive hat-wearing. All of these theories have been disproved. It’s also untrue that hair loss can be determined by looking at your maternal grandfather, or that 40-year-old men who haven’t lost their hair will never lose it.
The best candidates for hair replacement
A tube like instrument punches round grafts from the donar site to be placed in the area where hair replacement is desired.
A tube like instrument punches round grafts from the donar site to be placed in the area where hair replacement is desired.
Hair replacement surgery can enhance your appearance and your self-confidence, but the results won’t necessarily match your ideal. Before you decide to have surgery, think carefully about your expectations and discuss them with your surgeon. It’s important to understand that all hair replacement techniques use your existing hair. The goal of surgery is to find the most efficient uses for existing hair. Hair replacement candidates must have healthy hair growth at the back and sides of the head to serve as donor areas. Donor areas are the places on the head from which grafts and flaps are taken. Other factors, such as hair color, texture and waviness or curliness may also affect the cosmetic result. There are a number of techniques used in hair replacement surgery. Sometimes, two or more techniques are used to achieve the best results. Transplant techniques, such as punch grafts, mini grafts, micro-grafts, slit grafts and strip grafts are generally performed on patients who desire a more modest change in hair fullness. Flaps, tissue-expansion and scalp-reduction are procedures that are usually more appropriate for patients who desire a more dramatic change.
Remember, there are limits to what can be accomplished. An individual with very little hair might not be advised to undergo hair replacement surgery.
Hair loss in women
Some doctors estimate that one in five women will experience some degree of hair loss usually caused by aging, illness, or hormonal changes after menopause. Women tend to experience a subtle thinning all over the scalp rather than losing hair in patches as is common in men. To correct the problem, some women choose to wear a wig or hair extensions. Others have had some success using a topical prescriptive drug. The effectiveness of such drugs varies in some patients and simply prevents further hair loss without stimulating any appreciable new growth. Hair replacement surgery may be the answer for those who feel uncomfortable with either of these options.
Because mini-grafts are usually the surgical treatment of choice for filling in thinning areas, good candidates for this procedure should have dense hair growth at the back of the head. Mini-grafts are harvested from this dense area and replanted in thinning areas to create a fuller look. Occasionally flap and tissue expansion procedures may be used if the individual is judged to be a good candidate. If you’re considering a hair replacement procedure, it’s important to understand that you will never have the coverage you had prior to your hair loss, but surgery may camouflage the thin areas and give you more fullness.
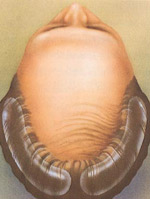
A tissue expander causes the skin of hair-bearing scalp to gradually expand.
All surgery carries some uncertainty and risk
A tissue expander causes the skin of hair-bearing scalp to gradually expand.
Hair replacement surgery is normally safe when performed by a qualified, experienced physician. Still, individuals vary greatly in their physical reactions and healing abilities, and the outcome is never completely predictable. As in any surgical procedure, infection may occur. Excessive bleeding and/or wide scars, sometimes called “stretch-back” scars caused by tension may result from some scalp-reduction procedures. In transplant procedures, there is a risk that some of the grafts won’t “take.” Although it is normal for the hair contained within the plugs to fall out before establishing regrowth in its new location, sometimes the skin plug dies and surgery must be repeated. At times, patients with plug grafts will notice small bumps on the scalp that form at the transplant sites. These areas can usually be camouflaged with surrounding hair.
When hair loss progresses after surgery, an unnatural, “patchy” look may result-especially if the newly placed hair lies next to patches of hair that continue to thin out. If this happens, additional surgery may be required.
Planning your surgery
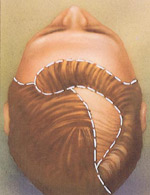
When the skin beneath the hair has stretched enough, it is surgically placed over the bald area.
When the skin beneath the hair has stretched enough, it is surgically placed over the bald area.
Hair replacement surgery is an individualized treatment. To make sure that every surgical option is available to you, find a doctor who has experience performing all types of replacement techniques-flaps and tissue expansion as well as transplants. Look elsewhere if your doctor tells you that he or she has perfected one technique that can “do it all.” In your initial consultation, your surgeon will evaluate your hair growth and loss, review your family history of hair loss, and find out if you’ve had any previous hair replacement surgery. Your surgeon will also ask you about your lifestyle and discuss your expectations and goals for surgery. Medical conditions that could cause problems during or after surgery, such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, blood-clotting problems, or the tendency to form excessive scars, should also be checked by your doctor. Be sure to tell your surgeon if you smoke or are taking any drugs or medications, especially aspirin or other drugs that affect clotting.
If you decide to have hair replacement surgery, your surgeon will explain anesthesia, the type of facility where the surgery will be performed, and the risks and costs involved. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor any questions. Make sure you understand your surgeon’s plan – which procedures will be used and how long each will take. Ask your doctor to give you an idea of what you will look like after the procedure or, in the case of grafts, after each stage of treatment.
Preparing for your surgery
Your surgeon will give you specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating and drinking, smoking, and taking and avoiding certain vitamins and medications. Carefully following these instructions will help your surgery go more smoothly. If you smoke, it’s especially important to stop at least a week or two before surgery; smoking inhibits blood flow to the skin, and can interfere with healing. You should arrange for someone to drive you home after your surgery. Plan to take it easy for a day or two after the procedure and arrange for assistance if you think you’ll need it.
Where your surgery will be performed
Hair replacement surgery is usually performed in a physician’s office-based facility or in an outpatient surgery center. Rarely does it require a hospital stay.
Types of anesthesia
Hair replacement surgery, no matter what technique is used, is usually performed using a local anesthesia along with sedation to make you relaxed and comfortable. Your scalp will be insensitive to pain, but you may be aware of some tugging or pressure. General anesthesia may be used for more complex cases involving tissue expansion or flaps. If general anesthesia is used, you’ll sleep through the procedure.
The surgery
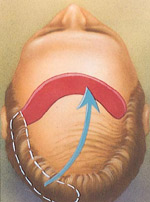
During flap surgery, a section of bald scalp is cut out and a flap of hairbearing skin is sewn into its place.
Hair transplantation involves removing small pieces of hair-bearing scalp grafts from a donor site and relocating them to a bald or thinning area. Grafts differ by size and shape. Round-shaped punch grafts usually contain about 10-15 hairs. The much smaller mini-graft contains about 2-4 hairs; and the micro-graft, 1-2 hairs. Slit grafts, which are inserted into slits created in the scalp, contain about 4-10 hairs each; strip grafts are long and thin and contain 30-40 hairs.
During flap surgery, a section of bald scalp is cut out and a flap of hairbearing skin is sewn into its place.
Generally, several surgical sessions may be needed to achieve satisfactory fullness-and a healing interval of several months is usually recommended between each session. It may take up to two years before you see the final result with a full transplant series. The amount of coverage you’ll need is partly dependent upon the color and texture of your hair. Coarse, gray or light-colored hair affords better coverage than fine, dark-colored hair. The number of large plugs transplanted in the first session varies with each individual, but the average is about 50. For mini-grafts or micro-grafts, the number can be up to 700 per session.
Just before surgery, the “donor area” will be trimmed short so that the grafts can be easily accessed and removed. For punch grafts, your doctor may use a special tube-like instrument made of sharp carbon steel that punches the round graft out of the donor site so it can be replaced in the area to be covered – generally the frontal hairline. For other types of grafts, your doctor will use a scalpel to remove small sections of hair-bearing scalp, which will be divided into tiny sections and transplanted into tiny holes or slits within the scalp. When grafts are taken, your doctor may periodically inject small amounts of saline solution into the scalp to maintain proper skin strength. The donor site holes may be closed with stitches-for punch grafts, a single stitch may close each punch site; for other types of grafts, a small, straight-line scar will result. The stitches are usually concealed with the surrounding hair. To maintain healthy circulation in the scalp, the grafts are placed about one-eighth of an inch apart. In later sessions, the spaces between the plugs will be filled in with additional grafts. Your doctor will take great care in removing and placement of grafts to ensure that the transplanted hair will grow in a natural direction and that hair growth at the donor site is not adversely affected.
After the grafting session is complete, the scalp will be cleansed and covered with gauze. You may have to wear a pressure bandage for a day or two. Some doctors allow their patients to recover bandage-free.
Plastic surgeons are the leaders in tissue expansion, a procedure commonly used in reconstructive surgery to repair burn wounds and injuries with significant skin loss. Its application in hair replacement surgery has yielded dramatic results-significant coverage in a relatively short amount of time.
In this technique, a balloon-like device called a tissue expander is inserted beneath hair bearing scalp that lies next to a bald area. The device is gradually inflated with salt water over a period of weeks, causing the skin to expand and grow new skin cells. This causes a bulge beneath the hair-bearing scalp, especially after several weeks.
When the skin beneath the hair has stretched enough – usually about two months after the first operation-another procedure is performed to bring the expanded skin over to cover the adjacent bald area. For more information about tissue expansion, ask your plastic surgeon for the ASPRS brochure entitled, Tissue Expansion: Creating New Skin from Old.
Flap surgery: Flap surgery on the scalp has been performed successfully for more than 20 years. This procedure is capable of quickly covering large areas of baldness and is customized for each individual patient. The size of the flap and its placement are largely dependent upon the patient’s goals and needs. One flap can do the work of 350 or more punch grafts.
The patterns used in scalp reduction vary widely, yet all meet the goal of bringing hair and scalp together to cover bald areas.
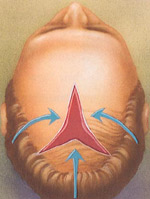
The patterns used in scalp reduction vary widely, yet all meet the goal of bringing hair and scalp together to cover bald areas.
A section of bald scalp is cut out and a flap of hair-bearing skin is lifted off the surface while still attached at one end. The hair-bearing flap is brought into its new position and sewn into place, while remaining tethered to its original blood supply.
As you heal, you’ll notice that the scar is camouflaged – or at least obscured – by relocated hair, which grows to the very edge of the incision.
In recent years, plastic surgeons have made significant advances in flap techniques combining flap surgery and scalp reduction for better coverage of the crown; or with tissue expansion, to provide better frontal coverage and a more natural hairline.
Scalp reduction: This technique is sometimes referred to as advancement flap surgery because sections of hair-bearing scalp are pulled forward or ” advanced” to fill in a bald crown.
Scalp reduction is for coverage of bald areas at the top and back of the head. It’s not beneficial for coverage of the frontal hairline. After the scalp is injected with a local anesthetic, a segment of bald scalp is removed. The pattern of the section of removed scalp varies widely, depending on the patient’s goals. If a large amount of coverage is needed, doctors commonly remove a segment of scalp in an inverted Y-shape. Excisions may also be shaped like a U, a pointed oval, or some other figure.
The skin surrounding the cut-out area is loosened and pulled, so that the sections of hair-bearing scalp can be brought together and closed with stitches. It’s likely that you’ll feel a strong tugging at this point, and occasional pain.
After your surgery

The result of hair replacement sugery can enhance your appearence and self-confidence.
The result of hair replacement sugery can enhance your appearence and self-confidence.
How you feel after surgery depends on the extent and complexity of the procedure. Any aching, excessive tightness, or throbbing can be controlled with pain medication prescribed by your physician. If bandages are used, they will usually be removed one day later. You may gently wash your hair within two days following surgery. Any stitches will be removed in a week to 10 days. Be sure to discuss the possibility of swelling, bruising and drainage with your surgeon. Because strenuous activity increases blood flow to the scalp and may cause your transplants or incisions to bleed, you may be instructed to avoid vigorous exercise and contact sports for at least three weeks. Some doctors also advise that sexual activity be avoided for at least 10 days after surgery. To make sure that your incisions are healing properly, your doctor will probably want to see you several times during the first month after surgery. It’s important that you carefully follow any advice you receive at these follow-up visits.
Getting back to normal
How soon you resume your normal routine depends on the length, complexity and type of surgery you’ve had. You may feel well enough to go back to work and resume normal, light activity after several days. Many patients who have had transplants (plugs or other grafts) are dismayed to find that their “new” hair falls out within six weeks after surgery. Remember, this condition is normal and almost always temporary. After hair falls out, it will take another five to six weeks before hair growth resumes. You can expect about a half-inch of growth per month.
Follow up procedures
You may need a surgical “touch-up” procedure to create more natural-looking results after your incisions have healed. Sometimes, this involves blending, a filling-in of the hairline using a combination of mini-grafts, micro grafts or slit grafts. Or, if you’ve had a flap procedure, a small bump called a “dog ear” may remain visible on the scalp. Your doctor can surgically remove this after complete healing has occurred. In general, it’s best to anticipate that you will need a touch-up procedure. Your surgeon can usually predict how extensive your follow-up surgery is likely to be.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Vein Removal
A salt solution is injected into varicose veins or tiny spider veins. They collapse and disappear within a few weeks.
Recovery: Back at work next day; no prolonged sitting or standing, or squatting, heavy lifting and jogging, for two weeks.
Comment: Treatments may require weeks or months. Varicose veins pencil size or larger may call for vascular surgery. Lasers are being used experimentally.
Risks: Blood clots, inflammation, allergic reaction, scarring, blotches, discoloration.
Permanence: Treated veins are gone; new ones may surface.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Scar Revision
This operation is performed to improve the appearance of scars.
There are many ways to perform scar revision surgery. The method must be tailored to the individual patient needs. The operation is done under either local anesthetic (you are awake) or general anesthetic (you are asleep). You can often choose. Most of the time this is an outpatient operation and a stay in the hospital is not needed.
All operations have some risk. The risks can be divided into two groups. First those that are seen in all operations and second those that are unique or special for this operation. In the first group, the main risks are swelling, bruising, bleeding, infection, a scar and numbness or change in feeling.
The main thing to remember about this operation is that the scar will not disappear after surgery. All scars are permanent. The aim is to make your scar less noticeable. In most cases there is about a 90% chance of improvement. Sometimes the scar looks about the same after surgery and there is minimal improvement. In rare cases the scar can be worse (<1%). True keloid scars are rarely improved with surgery alone and so it is important to distinguish between hypertrphic scars and keloids. Some surgeons feel that silicone or oil gel sheets applied to the scar after it has healed may improve the appearance. Sometimes steroid injections are used to reduce the amount of collagen in the wound. The recovery takes one to two weeks. Most people are back to work within a week or two. The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result. The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation. Please don't hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Tissue expansion
In order to allow the body to produce extra skin for use in other operations, a tissue expansion is required. It is one of the best methods to reconstruct damaged tissue.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have. This information is also available by email
Hand Surgery
Hand surgery
Dramatic advances have been made in recent years in treating patients with hand injuries, degenerative disorders, and birth defects of the hand to improve both function and appearance. Plastic surgeons (along with orthopedic surgeons and general surgeons) treat patients with a wide range of hand problems.
All surgery carries some uncertainty and risk. While the procedures are generally safe when performed by a qualified and experienced plastic surgeon, complications can arise. In all types of hand surgery, the possible complications include infection, poor healing, loss of feeling or motion, blood clots, and adverse reactions to the anesthesia. These complications are infrequent, and they can generally be treated.
Hand injuries
The most common procedures in hand surgery are those done to repair injured hands, including injuries to the tendons, nerves, blood vessels, and joints; fractured bones; and burns, cuts, and other injuries to the skin. Modern techniques have greatly improved the surgeon’s ability to restore function and appearance, even in severe injuries.
Among the techniques now used by plastic surgeons:
Grafting- the transfer of skin, bone, nerves, or other tissue from a healthy part of the body to repair the injured part;
Flap surgery-moving the skin along with its underlying fat, blood vessels, and muscle from a healthy part of the body to the injured site;
Replantation or transplantation-restoring accidentally amputated fingers or hands using microsurgery, an extremely precise and delicate surgery performed under magnification. Some injuries may require several operations over an extended period of time.
In many cases, surgery can restore a significant degree of feeling and function to injured hands. However, recovery may take months, and a period of hand therapy will most often be needed.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The carpal tunnel is a passageway through the wrist carrying tendons and one of the hand’s major nerves. Pressure may build up within the tunnel because of disease (such as rheumatoid arthritis), injury, fluid retention during pregnancy, overuse, or repetitive motions. The resulting pressure on the nerve within the tunnel causes a tingling sensation in the hand, often accompanied by numbness,
aching, and impaired hand function. This is known as carpal tunnel syndrome.
In some cases, splinting of the hand and anti-inflammatory medications will relieve the problem. If this doesn’t work, however, surgery may be required. The surgeon makes an incision from the palm to the wrist, providing access to the tissue that’s causing pressure on the nerve. He or she will then cut the tissue that’s pressing on the nerve, in order to release the pressure. A large dressing and splint are used after surgery to restrict motion and promote healing. The scar will gradually fade and become barely visible. A section of tissue is cut, relieving pressure on the nerve and restoring feeling and function to the hand. The results of the surgery will depend in part on how long the condition has existed and how much damage has been done to the nerve.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammation of the joints, is a disabling disease that can affect the appearance and the function of the hands and other parts of the body. It often deforms finger joints and forces the fingers into a bent position that hampers movement. Disabilities caused by rheumatoid arthritis can often be managed without surgery-for example, by wearing special splints or using physical therapy to strengthen weakened areas. For some patients, however, surgery offers the best solution. Surgeons can repair or reconstruct almost any area of the hand or wrist by removing tissue from inflamed joints, repositioning tendons, or implanting artificial joints. While your hand may not regain its full use, you can generally expect a significant improvement in function and appearance. Rheumatoid arthritis can continue to cause damage to your hand, sometimes requiring further surgery, and you’ll still need to see your rheumatologist for continuing care.
Dupuytren’s contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is a disorder of the skin and underlying tissue on the palm side of the hand. Thick, scar-like tissue forms under the skin of the palm and may extend into the fingers, pulling them toward the palm and restricting motion. The condition usually develops in mid-life and has no known cause (though it has a tendency to run in families).
The surgeon may make zig-zag incisions across this band of tissue, creating small skin flaps. Surgery is the only treatment for Dupuytren’s contracture. The surgeon will cut and separate the bands of thickened tissue, freeing the tendons and allowing better finger movement. The operation must be done very precisely, since the nerves that supply the hand and fingers are often tightly bound up in the abnormal tissue. In some cases, skin grafts are also needed to replace tightened and puckered skin. The results of the surgery will depend on the severity of the condition. You can usually expect significant improvement in function, particularly after physical therapy and a thin, fairly inconspicuous scar.
Congenital defects
Congenital deformities of the hand-that is, deformities a child is born with-can interfere with proper hand growth and cause significant problems in the use of the hand. Fortunately, with modern surgical techniques most defects can be corrected at a very early age-in some cases during infancy, in others at two or three years-allowing normal development and functioning of the hand.
One of the most common congenital defects is syndactyly, in which two or more fingers are fused together. Surgical correction involves cutting the tissue that connects the fingers, then grafting skin from another part of the body. (The procedure is more complicated if bones are also fused.) Surgery can usually provide a full range of motion and a fairly normal appearance, although the color of the grafted skin may be slightly different from the rest of the hand. If you need further information please read the detailed information that follows.
Other common congenital defects include short, missing, or deformed fingers, immobile tendons, and abnormal nerves or blood vessels. In most cases, these defects can be treated surgically and significant improvement can be expected.
Syndactly
What is it?
Syndactyly describes the joining together of two or more fingers, due to a failure of differentiation of parts in the upper limb. The separation failure occurs between the sixth to eighth week of intrauterine life, and the condition may recur in affected families.
How common is it?
Syndactyly is the commonest of all congenital hand deformities (i.e.. present at birth), with an incidence approaching 1/600 live births. The ring and middle fingers are the most frequently affected, followed by the little and ring, the middle and index, and the index and thumb.
The condition frequently presents as an isolated anomaly, but may occur in association with other conditions (e.g.. Apert’s syndrome, which also involves craniofacial malformations which are usually given surgical priority).
How is it classified?
Syndactyly is said to be complete when the entire web between two digits is fused, and incomplete when it is not. It is complex when the underlying bones of the fingers are also joined, and simple when only soft tissues are involved.
How is it treated?
The treatment of syndactyly is the surgical separation of the affected digits by a specialist in hand surgery.
When should the surgery be done?
It is advisable to perform surgery early, and one should aim to have all the webs divided before the child is subjected to peer curiosity at school. Joined fingers may adversely affect the growth of the hand, and there are situations (e.g.. webbing between the index and thumb) when surgery is performed sooner, to allow the natural development of hand function (grasping objects in infancy).
What are the principles of this type of surgery?
Although many different techniques have been described to treat syndactyly, all of them share the concept that a skin deficiency exists at the base of a fused web that has been fully separated. It is therefore usually necessary to introduce a skin graft taken from another part of the body, such as the groin which leaves a cosmetically acceptable scar. In order to re-surface the borders of affected digits using local tissue, several Z-shaped skin flaps are used, which result in a scar which has the shape of a zig-zag.
The surgical principles of syndactyly release are:
1: To provide a good web between the fingers
2: To provide adequate skin cover either side of the web space
3: To separate all tissues completely
4: To minimise the potential for later scar contracture
Other important aspects of the operation include:
1: The need to correct all skeletal abnormalities in the digits
2: The release of only one side of any digit at any one time
3: The need for meticulous dissection under loupe magnification
Skin grafts need to be immoblised to ‘take’, and the dressings following syndactyly release are often bulky and left in place for the first 7-14 days (depending on the climate: dressings are removed earlier in hot countries). It is frequent practice for the first change of dressing to be performed under general anaesthesia.
N.B. Sometimes an incomplete result is obtained at a first surgical setting, and a re-release of syndactyly is planned during adolescence.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Since the hand is a very sensitive part of the body, you may have mild to severe pain following surgery. Injections or oral medication will make you more comfortable.
How long your hand must remain immobilized and how quickly you resume your normal activities depends on the type and extent of surgery and on how fast you heal.
To enhance your recovery and give you the fullest possible use of your hand, your surgeon may recommend a course of rehabilitation (physical and occupational therapy) under the direction of a trained hand therapist. Your therapy may include hand exercises, heat and massage therapy, electrical nerve stimulation, splinting, traction, and special wrappings to control swelling.
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have
Calf Implants
Calf implants are placed in order to increase the size of the calves to make them more full and muscular. It involves making a small incision behind the knee and placing a pliable rubber implant next to the calf muscle, making the calf muscle bulge out more. The appearance is often quite natural, even during exercise, and it is often possible to return to all normal activities.
This surgery can usually be performed as an outpatient, and you can go home immediately after the operation. It can be done under local anesthesia, but most people choose to have sedation, to make them drowsy and more comfortable during the surgery. It generally requires approximately one hour per calf. The incision for placing the implants is quite small, and is in the thin skin behind the knee; pain after the surgery is therefore quite tolerable. There is discomfort in walking for a few days, similar to the muscle ache felt after a vigorous workout. During the surgery, of course, the area would be numb, and it would not hurt at all.
All surgery has some potential risks, including the risks of bleeding, allergy to the anesthetic, and infection. In this surgery, serious complications are quite rare.
All surgery has the risks of scarring, bleeding, and infection. The health risks from these are relatively minor in this surgery, although any of these problems could necessitate removal of the implants.
Your calves will be pretty sore for the first few days after surgery, and you may want to stay home from work.
Most normal activities can be resumed within a few days, although your legs will be stiff and sore. You should avoid strenuous use of the legs for at least 6 weeks in order to give things a chance to heal up properly.
What benefit could I expect from the surgery?
If you are self-conscious about your calves, then this surgery can open up many new possibilities for changing your image, and can allow you to show off your legs in shorts, bathing suits, etc. As with most cosmetic surgery, the benefit you derive will depend upon the change in attitude that you will have about yourself as a result of the surgery.
The results are often quite long lasting, but you should view this as a temporary augmentation. You may have some problems with the implants or with your legs in the future, which would necessitate removal of the implants. (With age, the circulation in the legs gets less, and you will probably want to remove the implants if you start to have problems with your circulation).
The information on this web site is only intended as an introduction to this procedure and should not be used to determine whether you will have the procedure performed nor as a guarantee of the result.
The best method of determining your personal options is to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Makki. He will be able to answer specific questions related to your situation.
Please don’t hesitate to call for any questions that you might have

 Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Google +
Google +